Marformer: A Transformer for Predicting
Missing Data Distributions
Introducing Marformer
We propose a Transformer-based architecture that directly predicts posterior marginal distributions for missing data without fitting an explicit generative model. Inspired by BERT's masked language modeling, our approach trains on artificially masked observed values to learn dependencies in the data. Unlike generative approaches that model joint distributions, we focus exclusively on the posterior marginals needed for downstream decisions, enabling more direct optimization and avoiding the complexity of full generative modeling.
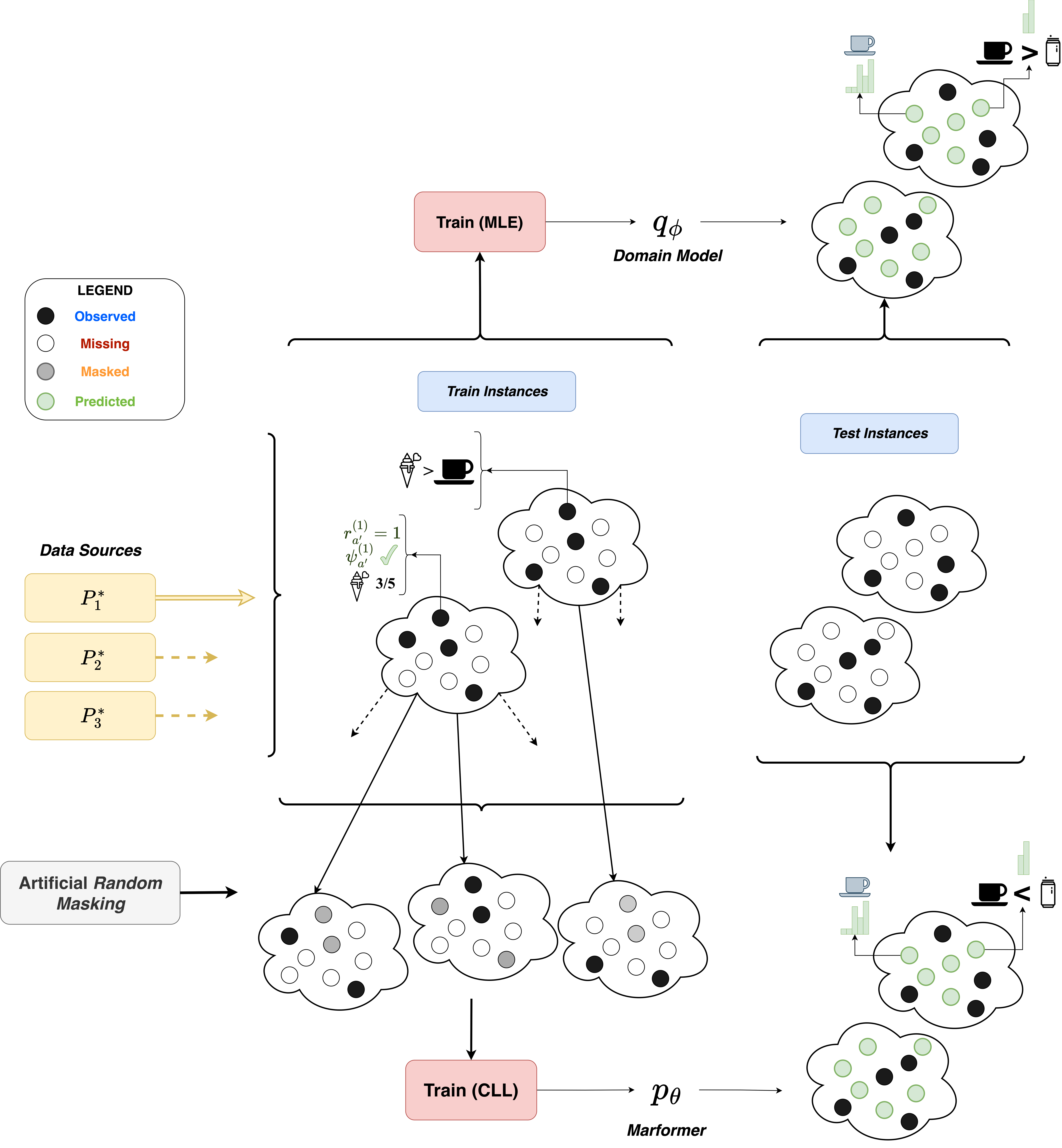
The design for the experiments presented in this paper. Each domain, parametrized by its attributes, acts as data source to generate Missing-at-Random (MAR) instances. The Marformer uses masked auto-encoding to get pθ that approximates the posterior marginals. We compare against baselines that are parametrized by learned qφ on the observed examples.
Architecture
The Marformer is a Transformer encoder that processes structured attributes through compositional embeddings. Each attribute's initial representation combines missingness indicators, type embeddings, observed values, and learned positional embeddings. Through multiple layers of cross-attention, the model iteratively refines its predictions by attending to other distributions, similar to message-passing algorithms but with learned refinement procedures.
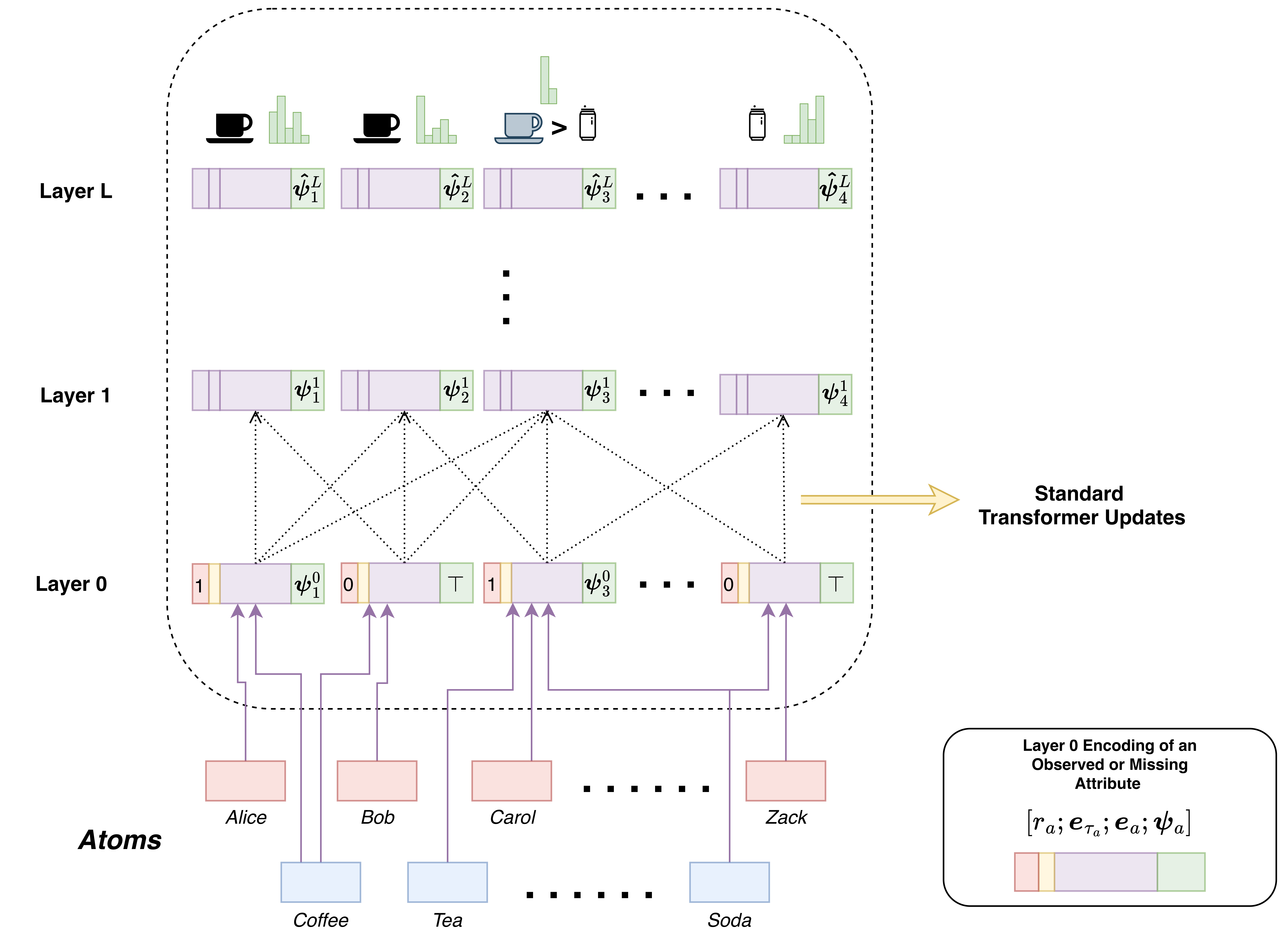
Architecture of Marformer, which is a Transformer encoder. The input is represented at layer 0 with unordered input tokens, one per attribute. Each token is transformed through L layers of cross-attention to yield refined predictions at the top layer.
Results
- Bayesian Networks and Multivariate Gaussians: Marformer consistently outperforms EM methods across both MCAR and Sequential MAR settings, even when EM has access to the true generative model structure. Classical methods suffer from local optima, while Marformer achieves lower KL divergence with sufficient training data.
- Real Dialogue Annotation Data: On HANNA and LLM-Rubric datasets, Marformer significantly outperforms the baseline MLP method (LLM-Rubric) in terms of log loss, RMSE, and correlation metrics (Pearson, Spearman, Kendall), demonstrating superior ability to learn correlations between LLM and human annotators.
- Structured Ratings and Rankings: In the complex annotation domain with hierarchical ordinal ratings and Bradley-Terry pairwise rankings, Marformer outperforms the Stan MCMC baseline, which has explicit knowledge of how ratings and rankings are generated. Marformer achieves better predictive performance while being orders of magnitude faster.